
The Mediterranean diet is a dietary pattern inspired by the traditional eating habits of countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. It emphasizes consuming plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. The diet also includes moderate consumption of dairy products, fish, and poultry, while red meat and sweets are limited. The Mediterranean diet is particularly renowned for its high content of healthy fats, mainly derived from olive oil and omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. This type of diet is associated with numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and enhanced cognitive function and mental health. The abundance of antioxidants, polyphenols, and omega-3 fatty acids from sources like olive oil and fatty fish contribute to these positive effects. Additionally, the Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods and limited intake of refined sugars and unhealthy fats makes it a well-rounded and nourishing diet plan for overall health and well-being.
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that has gained popularity for its potential health benefits. The macronutrient breakdown of the keto diet typically consists of around 75% fat, 20% protein, and 5% carbohydrates.
The main principle of the keto diet is to restrict carbohydrate intake to such a low level that the body enters a state of ketosis. Ketosis occurs when the body doesn’t have enough carbohydrates to burn for energy and instead relies on fat for fuel. This metabolic state leads to increased production of ketones, which are used as an alternative source of energy.
Foods that are prioritized on the keto diet include healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and coconut oil. Proteins from sources like meat, fish, and eggs are also consumed in moderation. Foods to avoid include starchy vegetables, grains, legumes, sugary products, and most fruits, as they are high in carbohydrates.
Many studies suggest that the keto diet may have several health benefits. These include improved insulin sensitivity, reduced triglyceride levels, and potential weight loss due to increased fat burning. However, it’s important to note that the keto diet may not be suitable for everyone and should be followed under medical advice.
In conclusion, the keto diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that aims to induce ketosis in the body. It has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, but it’s essential to consider individual needs and seek professional advice before embarking on this diet.
Both the Mediterranean and ketogenic diets have been associated with cognitive health and mood benefits. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and olive oil, has been linked to improved cognitive function and reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases. This diet is high in omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which support brain function and mood regulation.
The ketogenic diet, on the other hand, promotes mental well-being by stabilizing blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation. By restricting carbohydrate intake, the keto diet improves insulin sensitivity and reduces the risk of metabolic syndrome, a condition linked to cognitive impairment and mood disorders. The diet also encourages the consumption of healthy fats, such as avocados and coconut oil, which provide essential nutrients for brain health.
In summary, both the Mediterranean and ketogenic diets have potential benefits for cognitive function and mood. While the Mediterranean diet emphasizes a balanced and diverse array of nutrient-rich foods, the keto diet focuses on low carbohydrate intake and increased healthy fat consumption. It is important to note that individual needs may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable before making any significant dietary changes.
The Mediterranean diet is well-known for its many health benefits, including its positive impact on cognitive function and mood. This diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats, has been associated with a reduced risk of cognitive decline and certain neurodegenerative diseases. The Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on antioxidant-rich foods, such as leafy greens and berries, helps to protect brain cells from damage caused by inflammation and oxidative stress. Additionally, the diet’s moderate consumption of fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon and sardines, provides omega-3 fatty acids that are essential for brain health. The Mediterranean diet’s overall focus on a healthy, balanced eating pattern also contributes to better overall physical health, which in turn can positively impact cognitive functioning and mood.
Omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in supporting overall cognitive and mood health. These essential fats are crucial for maintaining optimal brain function and are known to help with cognitive function and mood balance.
Numerous studies have shown that regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids is associated with better cognitive function and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases. These healthy fats support the growth and development of brain cells and help promote communication between brain cells, which is essential for cognitive processes such as memory, attention, and learning.
Dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, as well as plant sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Incorporating these foods into your diet can provide your body with the omega-3 fatty acids it needs to support your brain health.
In conclusion, omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for maintaining cognitive function and mood balance. Including dietary sources of omega-3s in your diet can provide numerous benefits for brain health. So, be sure to incorporate omega-3-rich foods into your meals to support optimal cognitive and mood health.
Including leafy vegetables in both the Mediterranean and Keto diets can provide numerous benefits for brain health and help slow cognitive decline. These vegetables are rich in nutrients such as lutein, folate, and beta-carotene, which have been linked to improved brain function and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Lutein, a powerful antioxidant found in leafy greens, has been shown to accumulate in the brain and has a protective effect on cognitive function. It may help prevent age-related cognitive decline and improve memory and processing speed.
Folate, another essential nutrient found in leafy greens, plays a vital role in brain health. It helps produce neurotransmitters that regulate mood and cognitive function. Low levels of folate have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment.
Beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A found in leafy vegetables, also has antioxidant properties and may help reduce inflammation in the brain, supporting overall cognitive health.
Some examples of leafy greens that can be included in the Mediterranean and Keto diets are kale, spinach, Swiss chard, collard greens, and arugula. These vegetables are versatile and can be incorporated into various dishes, ensuring a diverse and nutrient-dense diet.
Incorporating leafy vegetables into your diet, whether through the Mediterranean or Keto approach, can provide essential nutrients that support brain health and slow cognitive decline. So make sure to include a generous serving of these greens in your daily meals.
In addition to leafy greens, starchy vegetables also play a significant role in promoting cognitive health and mood. Vegetables such as potatoes, sweet potatoes, and winter squash provide essential nutrients like complex carbohydrates and fiber, which are beneficial for brain function and overall well-being.
Complex carbohydrates found in starchy vegetables are a key source of energy for the brain. They are slowly digested, resulting in a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream. This helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can negatively impact cognitive function and mood.
Fiber, another important component of starchy vegetables, supports brain health by promoting healthy digestion and regulating blood sugar levels. It also helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease, which can have a negative impact on cognitive function.
Both the Mediterranean and Keto diets can incorporate starchy vegetables to enhance cognitive and mood benefits. The Mediterranean diet includes moderate consumption of starchy vegetables, while the Keto diet allows for limited intake due to its low-carbohydrate nature. However, there are ways to include small portions of starchy vegetables in the Keto diet by carefully managing overall carbohydrate intake.
By incorporating starchy vegetables into both diets, individuals can reap the benefits of complex carbohydrates and fiber, supporting brain function and mood stability.
Oily fish, such as salmon, herring, sardines, tuna, and mackerel, are not only delicious but also beneficial for cognitive health. These fish are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for brain function and can help protect against cognitive decline.
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are crucial for the structure and function of brain cells. They are known to play a vital role in maintaining optimal cognitive function and supporting overall brain health. Research suggests that a higher intake of omega-3 fatty acids from oily fish is associated with a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and dementia.
These fatty acids are thought to provide neuroprotective effects, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. They are also believed to promote the growth and development of new brain cells, improving memory and cognitive performance.
Incorporating oily fish into your diet, whether through the Mediterranean or ketogenic diet, can provide an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids for brain health. Aim to include oily fish in your meals at least twice a week to maximize cognitive benefits. So, whether you’re enjoying a salmon salad or savoring grilled mackerel, you’re doing your brain a favor by fueling it with essential omega-3 fatty acids.
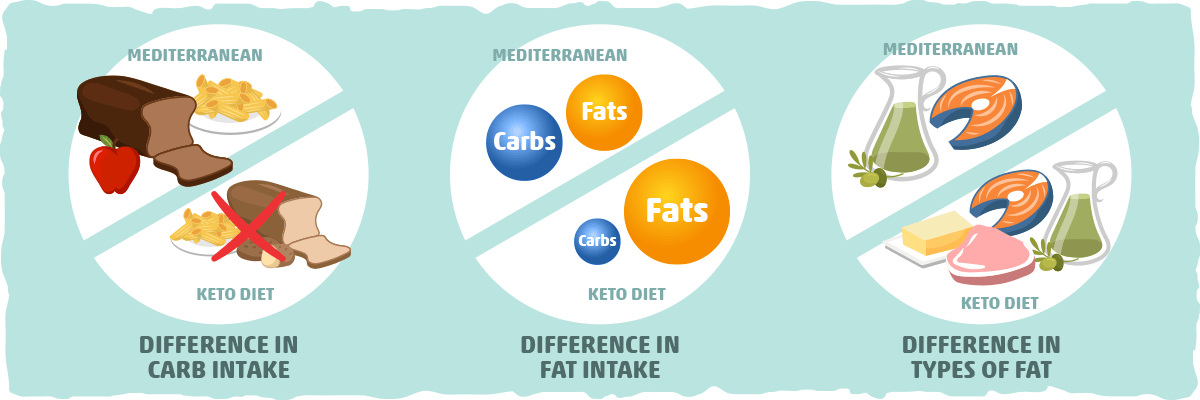
When it comes to carbohydrate intake and refined sugars, the Mediterranean diet and ketogenic diet differ significantly. The ketogenic diet is characterized by a strict restriction of carbohydrate intake to less than 50 grams per day, relying primarily on fats for energy. On the other hand, the Mediterranean diet includes high-quality carbohydrates from whole foods like whole grains, legumes, and fruits.
One of the key ways the Mediterranean diet moderates sugar intake is by emphasizing other fresh, nutrient-dense foods. While the diet does allow for moderate consumption of sweets and desserts, it prioritizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This approach ensures a variety of essential nutrients while limiting the intake of refined sugars.
In contrast, the ketogenic diet strictly limits sugar consumption, removing most sources of refined sugars from the meal plan. This includes sugary drinks, candies, desserts, and processed foods that contain added sugars. The emphasis on fat consumption and low-carbohydrate intake in the keto diet helps regulate blood sugar levels and can be beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or those looking to reduce their sugar intake.
In summary, the Mediterranean diet includes a moderate amount of high-quality carbohydrates from whole foods, while the ketogenic diet restricts carbohydrate intake to very low levels. Both diets provide different approaches to managing sugar consumption, and individuals may choose the one that aligns with their health goals and preferences.
The ketogenic diet, commonly known as the keto diet, has gained popularity for its potential cognitive benefits. This low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet has been shown to improve brain function and support mental health. By reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the keto diet encourages the body to enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fats for energy instead of carbohydrates. This metabolic state has been associated with improved cognitive function, increased focus, and enhanced mental clarity. Additionally, the keto diet may provide neuroprotective benefits, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. While further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of the keto diet on cognitive health, early indications suggest that it may be a promising dietary approach for supporting brain function and overall mental well-being.
Low-fat diets have the potential to offer numerous cognitive benefits and contribute to overall mental health. Research suggests that these diets may play a preventative role in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Consumption of fats, particularly saturated and trans fats, has been linked to impaired cognitive function and an increased risk of these diseases. In contrast, low-fat diets tend to emphasize the consumption of complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and fruits and vegetables, which provide essential nutrients for brain health.
Maintaining a balanced fat intake is crucial for optimal brain function. Healthy fats, such as those found in fatty fish, avocados, and nuts, are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been associated with improved cognitive function and mental health.
While low-fat diets have their potential benefits, it is important to consider the risks as well. Fat is an essential macronutrient and plays a vital role in various bodily processes. Severe restrictions on fat consumption can lead to deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids, which are necessary for cognitive health.
In conclusion, low-fat diets have the potential to positively influence cognitive function and mental health. However, it is crucial to maintain a balanced approach to fat intake and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice.
A growing body of research suggests that ketogenic diets may have potential benefits for neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
A ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that promotes the production of ketones in the body as an alternative source of energy. This metabolic state has been shown to have therapeutic effects on various health conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases.
In Alzheimer’s disease, there is a progressive decline in cognitive function, memory loss, and the accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain. Studies have shown that a ketogenic diet can help reduce the production of amyloid plaques and improve cognitive function in animal models. It is believed that ketones provide an alternative fuel source for brain cells that are unable to utilize glucose effectively in Alzheimer’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. Research indicates that a ketogenic diet may help protect these neurons and improve motor function in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. It is thought that the ketones produced during ketosis have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which can help reduce neuronal damage.
Several studies have provided supportive evidence for the relationship between ketogenic diets and neurodegenerative diseases. For instance, a study published in the journal Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience found that a ketogenic diet improved memory and reduced amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.
While more research is needed to fully understand the impact of ketogenic diets on neurodegenerative diseases in humans, the existing evidence suggests that they may have potential benefits. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before making any dietary changes, especially for individuals with existing medical conditions.
The Mediterranean diet is known for its numerous health benefits, including its positive impact on overall cognitive function and mood. This diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats, such as olive oil and nuts. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes moderate consumption of red wine, which is also believed to have mood-boosting effects in moderation. Research suggests that the Mediterranean diet may help reduce the risk of depression and improve overall mental well-being. The abundance of antioxidants, polyphenols, and omega-3 fatty acids in this diet’s key components, such as fatty fish and leafy greens, contribute to its potential mood-enhancing effects. Additionally, the Mediterranean diet’s focus on unprocessed, whole foods and avoidance of refined sugars and processed foods may help stabilize blood sugar levels and support a more balanced mood.
Consuming healthy fats has been linked to numerous mental health improvements. These fats play a crucial role in supporting brain function and regulating mood, making them an essential part of a healthy diet.
One of the main benefits of healthy fats is their impact on cognitive function. Omega-3 fatty acids found in foods such as oily fish, nuts, and eggs have been shown to enhance brain health and improve cognitive performance. These fats are particularly important for maintaining optimal brain function and preventing cognitive decline.
Healthy fats also play a role in mood regulation. Research suggests that diets rich in healthy fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. They provide the brain with the necessary nutrients to promote the production of neurotransmitters that regulate mood, such as serotonin and dopamine.
Sources of healthy fats include olive oil, which is a staple of the Mediterranean diet. Nuts, such as almonds and walnuts, are also excellent sources of healthy fats. Oily fish, like salmon and sardines, provide omega-3 fatty acids along with other beneficial nutrients. Avocados are another great source of healthy fats, as they contain monounsaturated fats that support brain health. Lastly, eggs provide omega-3 fatty acids and other essential nutrients that contribute to cognitive function.
Incorporating these sources of healthy fats into your diet can have a positive impact on mental health. By including olive oil, nuts, oily fish, avocados, and eggs in your meals, you can support brain function and regulate mood, ultimately leading to improved mental well-being.
Leafy greens, such as kale and spinach, have been extensively studied for their heart health and blood pressure improvement benefits. These green vegetables are not only low in calories but also rich in essential nutrients that support cardiovascular health.
Leafy greens are packed with nutrients like potassium, which plays a key role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Potassium helps to balance the effects of sodium, reducing its negative impact on blood pressure. Nitrates, another nutrient found in leafy greens, have also been shown to have a positive effect on blood pressure. Nitrates are converted into nitric oxide in the body, which helps relax and widen blood vessels, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure.
Including leafy greens in your diet is important for both the Mediterranean and ketogenic diets. In the Mediterranean diet, leafy greens are a staple and are consumed in abundance. They provide a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health. Similarly, in the ketogenic diet, leafy greens are an essential component for obtaining necessary nutrients while maintaining low carbohydrate intake.
Incorporating leafy greens into your diet is a simple but effective way to support heart health and improve blood pressure. Whether you follow the Mediterranean or ketogenic diet, these nutrient-dense vegetables can provide numerous health benefits, making them an excellent addition to any healthy eating plan.
You must be logged in to post a comment.